|
In-situ Tests |
Electrical Resistivity of soil
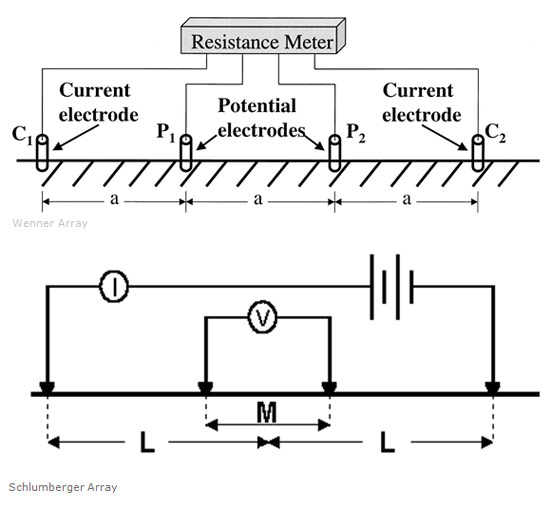
Soil electrical resistivity indicates the relative capability of the soil to conduct electrical current and it is a main indicator in determining corrosiveness of the soil. This is generally recognized as the most significant soil characteristic with regard to corrosivity of the soil. Soil resistivity can change dramatically with moisture content. Soil, which has a high resistivity when it is dry, can have substantially lower resistivity when it is wet or saturated depending on factors such as pH and chemical content. AHAM measures Electrical Resistivity using the SYSCAL IRIS Pro. There are many test arrangements (array) for the identification of the electrical resistivity of the soil, however the most common types are the Wenner (4-Pin) Array and the Schlumberger Array.
|
 |
| |
|
|